Capture User Feedback with Trace Annotations
In this tutorial, we'll build a simple LLM application and learn how to capture user feedback using Agenta's annotation system. By the end, you'll be able to:
- Create a simple LLM application with proper instrumentation
- Capture structured feedback about LLM responses
- View this feedback in the Agenta UI
This approach helps you collect valuable user insights and improve your LLM applications over time.
# Install required packages
# agenta - for tracing and annotation
# openai - for LLM API access
# opentelemetry.instrumentation.openai - for automatic tracing of OpenAI calls
%pip install agenta -q
%pip install openai -q
%pip install opentelemetry.instrumentation.openai -q
# Import necessary libraries
import os
import requests
# Agenta SDK for tracing and instrumentation
import agenta as ag
# OpenAI client and automatic instrumentation
import openai
from openai import OpenAI
from opentelemetry.instrumentation.openai import OpenAIInstrumentor
# Set up environment variables for API keys
# Note: Replace these with your actual API keys
os.environ["AGENTA_API_KEY"] = "your_agenta_api_key_here"
os.environ["AGENTA_HOST"] = "https://cloud.agenta.ai" # Use your self-hosted URL if applicable
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "your_openai_api_key_here"
# Set up instrumentation for tracing
# This automatically adds tracing to all OpenAI API calls
OpenAIInstrumentor().instrument()
# Initialize the Agenta SDK with your credentials
ag.init()
Creating a Function to Add Annotations
Annotations allow you to add structured feedback to your LLM application traces. To create an annotation, you need:
- Invocation details: The
trace_idandspan_idof the span you want to annotate - Annotation data: The feedback you want to add (scores, comments, labels, etc.)
- Evaluator slug: A name for the type of evaluation you're performing
When you use an evaluator for the first time, Agenta automatically creates it and infers its schema from your data. Later annotations using the same evaluator will be validated against this schema.
def annotate(trace_id, span_id, annotation, evaluator_slug):
"""Create an annotation for a specific trace/span with evaluation data.
Args:
trace_id: The ID of the trace to annotate
span_id: The ID of the span to annotate
annotation: Dictionary containing evaluation data (scores, comments, etc.)
evaluator_slug: Identifier for the evaluator (creates one if it doesn't exist)
Returns:
The annotation response data if successful, None otherwise
"""
# Set up request headers
headers = {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"Authorization": f"ApiKey {os.environ['AGENTA_API_KEY']}",
}
# Structure the annotation data according to the API format
annotation_data = {
"annotation": {
"data": {"outputs": annotation}, # Your feedback data goes here
"references": {"evaluator": {"slug": evaluator_slug}}, # Evaluator reference
"links": {"invocation": {"trace_id": trace_id, "span_id": span_id}}, # Link to the trace
}
}
# Send the annotation to the Agenta API
response = requests.post(
f"{os.environ.get('AGENTA_HOST', 'https://cloud.agenta.ai')}/api/preview/annotations/",
headers=headers,
json=annotation_data,
)
# Handle the response
if response.status_code == 200:
print("Annotation created successfully")
return response.json()
else:
print(f"Error creating annotation: {response.status_code}")
print(response.text)
return None
Putting It All Together
Now we'll create a simple LLM application that generates a story and adds user feedback as an annotation.
In a real application, you would typically:
- Get the
trace_idandspan_idfrom your application's instrumentation - Collect feedback from your users
- Create annotations with this feedback
For this tutorial, we'll use the @ag.instrument() decorator to create a traced function and manually add feedback.
@ag.instrument() # This decorator creates a root span for tracking the entire function
def generate(topic: str):
"""Generate a story about the given topic and add feedback as an annotation.
Args:
topic: The subject of the story to generate
Returns:
The generated story text
"""
# Create an OpenAI client
client = OpenAI()
# Generate a story about the provided topic
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-3.5-turbo",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."},
{
"role": "user",
"content": f"Write a short story about {topic}.",
},
],
)
# In a real application, you would obtain trace_id and span_id dynamically
# using one of these methods:
# Method 1: Get the current span context
# span_ctx = ag.tracing.get_span_context()
# trace_id = f"{span_ctx.trace_id:032x}" # Format as hexadecimal
# span_id = f"{span_ctx.span_id:016x}" # Format as hexadecimal
# Method 2: Use the helper function
link = ag.tracing.build_invocation_link()
trace_id = link.trace_id
span_id = link.span_id
# Add feedback annotation (simulating user feedback)
annotate(
trace_id=trace_id,
span_id=span_id,
annotation={
"score": 5, # Numerical score (1-5)
"comment": "This is a comment" # Text feedback
},
evaluator_slug="score-evaluator" # Creates this evaluator if it doesn't exist
)
# Return the generated story
return response.choices[0].message.content
# Test our function by generating a story about AI
generate(topic="AI")
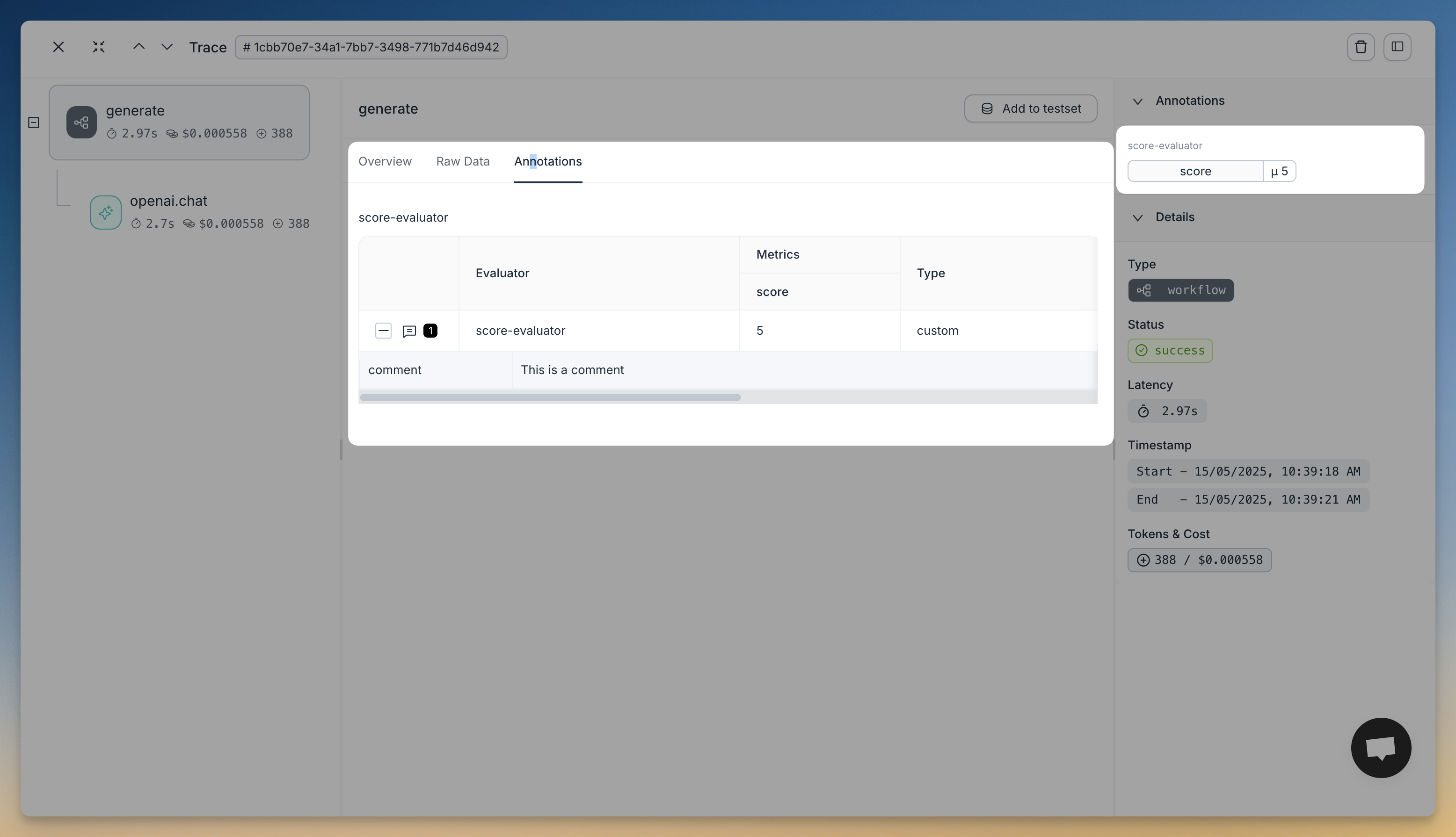
Viewing Annotations in the Agenta UI
After running the code above, you can view your annotations in the Agenta UI. Navigate to the Traces section and find the trace for your story generation. You'll see the annotation with the score and comment we added.
Here's an example of what this looks like in the UI:
Next Steps
Now that you understand how to add annotations to your traces, you can:
- Integrate annotation collection into your user-facing applications
- Create different evaluator types for different aspects of feedback
- Use the collected feedback to improve your prompts and models
